- Регистрация
- 9 Май 2015
- Сообщения
- 1,486
- Баллы
- 155
Intro
If you’re developing in Delphi and looking for a powerful, flexible, and highly customizable data grid solution, then is the perfect choice. In this blog post, we'll delve into how the grid can be configured to permanently show a filter row. The filter row allows you to quickly narrow down to the data you are interested in. Whether you're building an enterprise-level application, a desktop app, or a web-based solution, the TMS FNC Data Grid is equipped with robust features designed to enhance the user experience and make data interaction seamless.
Filtering
The filter row is a feature that can be used to apply filtering in the grid. To understand more about filtering, read through this blog post first:

Filter Row
If you already have data in the grid, you might need to start off by inserting a new row, making sure the filter editors are not covering potential data that needs to be taken into account when filtering. Typically, the filter row is part of the fixed rows. If you have a fixed row containing headers, it might be useful to add another fixed row.
Grid.FixedRowCount := 2;
Grid.InsertRow(1);
Enabling the filter row on top of the filter drop-down (available by default) is easy. We enable filtering first, then specify which kinds of filter options we want for runtime filtering and then specify which row needs to be allocated to show the filter options.
Grid.Options.Filtering.Enabled := True;
Grid.Options.Filtering.Controls := [gfcButton, gfcEditor];
Grid.Options.Filtering.Row := 1;
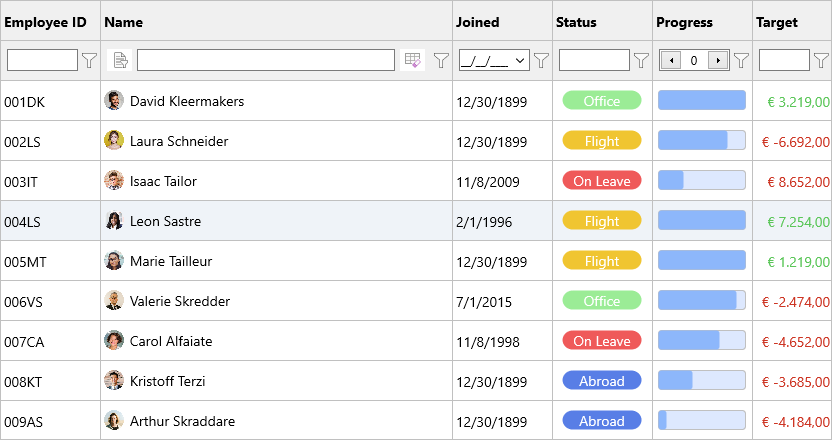
By default, enabling a filter row automatically detects which kind of editor is required. This can be customized at column level by using the following code.
Grid.ColumnByHeader('Joined').AddSetting(gcsFilterEditorType);
Grid.ColumnByHeader('Joined').FilterEditorType := gfetDateTime;
The following types are available
Additionally, when the column width is sufficiently large, a filter type selector and a clear button will appear.
Example 1
In this example, we specified a Status column filter
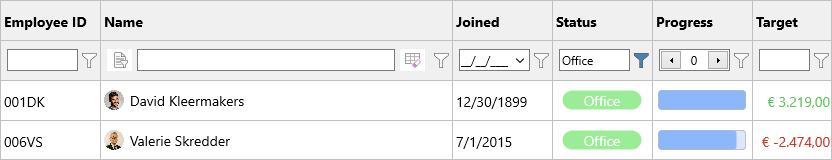
Programmatically, this corresponds with the following code
Grid.RemoveFilter;
f := Grid.Filter.ColumnFilter[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Status')];
f.&Type := gftEqual;
f.BuildCondition('Office');
Grid.ApplyFilter;
Example 2
In our second example, we use a different filter type, selectable with the drop-down list, next to the filter editor.
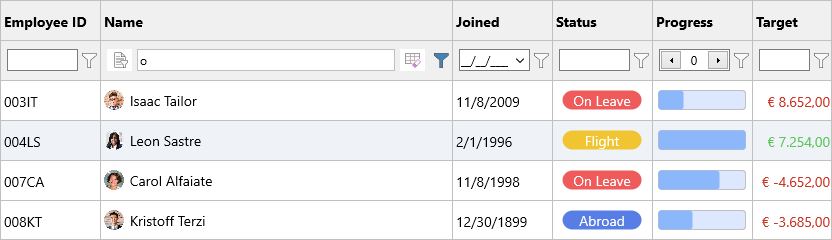
Programmatically, this corresponds with the following code
Grid.RemoveFilter;
f := Grid.Filter.ColumnFilter[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Name')];
f.&Type := gftContains;
f.BuildCondition('o');
Grid.ApplyFilter;
Custom Filter Editor
When you are in need for a custom filter editor, you can select the filter type gfetCustom, which enables you to create your own editor via the OnCreateCustomFilterEditor event. Below is a sample to create a combobox which filters the progress column via a selection of ranges.
Grid.BeginUpdate;
Grid.RemoveFilterEditor(MakeCell(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress'), 1));
Grid.Columns[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress')].FilterEditorType := gfetCustom;
Grid.Columns[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress')].AddSetting(gcsFilterEditorType);
Grid.EndUpdate;
When we implement the OnCreateCustomFilterEditor you can create an instance of the control of your choice, set content and bind events for filtering purposes
function TForm1.GridCreateCustomFilterEditor(Sender: TObject;
ACell: TTMSFNCDataGridCellCoord): TTMSFNCDataGridCellControl;
var
cbo: TComboBox;
begin
Result := TComboBox.Create(nil);
cbo := TComboBox(Result);
cbo.Items.Add('');
cbo.Items.Add('<= 25');
cbo.Items.Add('> 25 & <= 50');
cbo.Items.Add('> 50 & <= 75');
cbo.Items.Add('> 75');
cbo.OnChange := DoComboChange;
end;
procedure TForm1.DoComboChange(Sender: TObject);
var
cbo: TComboBox;
f: TTMSFNCDataGridDataFilterData;
begin
cbo := TComboBox(Sender);
Grid.RemoveFilter;
f := Grid.Filter.ColumnFilter[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress')];
f.Condition := cbo.Text;
Grid.ApplyFilter;
end;

Chaining Filters
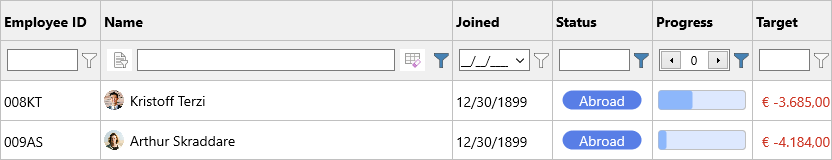
With the filter row as an option on top of the already built-in filtering features there are plenty of ways to browse through the data. If visual filtering is not applicable to your application, programmatic filtering can be an option and in this area we provide a way to chain filter operations together. Let's take the following example, where we find if the Name contains 'k', the Status equals 'Abroad' and the Progress is smaller than 50.
Grid.ClearFilter;
Grid.Filter.Add(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Name'), gftContains, 'k')
.&And(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Status'), gftEqual, 'Abroad')
.&And(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress'), gftSmallerThan, '50');
Grid.ApplyFilter;
Conclusion
TMS FNC Data Grid offers powerful filter options including a filter row. This feature allows you to quickly narrow down the data you are interested in. TMS FNC Data Grid is part of the .
If you’re developing in Delphi and looking for a powerful, flexible, and highly customizable data grid solution, then is the perfect choice. In this blog post, we'll delve into how the grid can be configured to permanently show a filter row. The filter row allows you to quickly narrow down to the data you are interested in. Whether you're building an enterprise-level application, a desktop app, or a web-based solution, the TMS FNC Data Grid is equipped with robust features designed to enhance the user experience and make data interaction seamless.
Filtering
The filter row is a feature that can be used to apply filtering in the grid. To understand more about filtering, read through this blog post first:

Filter Row
If you already have data in the grid, you might need to start off by inserting a new row, making sure the filter editors are not covering potential data that needs to be taken into account when filtering. Typically, the filter row is part of the fixed rows. If you have a fixed row containing headers, it might be useful to add another fixed row.
Grid.FixedRowCount := 2;
Grid.InsertRow(1);
Enabling the filter row on top of the filter drop-down (available by default) is easy. We enable filtering first, then specify which kinds of filter options we want for runtime filtering and then specify which row needs to be allocated to show the filter options.
Grid.Options.Filtering.Enabled := True;
Grid.Options.Filtering.Controls := [gfcButton, gfcEditor];
Grid.Options.Filtering.Row := 1;

By default, enabling a filter row automatically detects which kind of editor is required. This can be customized at column level by using the following code.
Grid.ColumnByHeader('Joined').AddSetting(gcsFilterEditorType);
Grid.ColumnByHeader('Joined').FilterEditorType := gfetDateTime;
The following types are available
- gfetAutomatic: Automatically detects the value type and chooses one of the other types.
- gfetString: A standard edit for string based values
- gfetBoolean: A checkbox for boolean based values
- gfetDateTime: A date/time picker for TDateTime based values
- gfetFloat: A spinbox for float values
- gfetNumber: A spinbox for number values
- gfetCustom: Specify your own editor
Additionally, when the column width is sufficiently large, a filter type selector and a clear button will appear.
Example 1
In this example, we specified a Status column filter

Programmatically, this corresponds with the following code
Grid.RemoveFilter;
f := Grid.Filter.ColumnFilter[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Status')];
f.&Type := gftEqual;
f.BuildCondition('Office');
Grid.ApplyFilter;
Example 2
In our second example, we use a different filter type, selectable with the drop-down list, next to the filter editor.

Programmatically, this corresponds with the following code
Grid.RemoveFilter;
f := Grid.Filter.ColumnFilter[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Name')];
f.&Type := gftContains;
f.BuildCondition('o');
Grid.ApplyFilter;
Custom Filter Editor
When you are in need for a custom filter editor, you can select the filter type gfetCustom, which enables you to create your own editor via the OnCreateCustomFilterEditor event. Below is a sample to create a combobox which filters the progress column via a selection of ranges.
Grid.BeginUpdate;
Grid.RemoveFilterEditor(MakeCell(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress'), 1));
Grid.Columns[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress')].FilterEditorType := gfetCustom;
Grid.Columns[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress')].AddSetting(gcsFilterEditorType);
Grid.EndUpdate;
When we implement the OnCreateCustomFilterEditor you can create an instance of the control of your choice, set content and bind events for filtering purposes
function TForm1.GridCreateCustomFilterEditor(Sender: TObject;
ACell: TTMSFNCDataGridCellCoord): TTMSFNCDataGridCellControl;
var
cbo: TComboBox;
begin
Result := TComboBox.Create(nil);
cbo := TComboBox(Result);
cbo.Items.Add('');
cbo.Items.Add('<= 25');
cbo.Items.Add('> 25 & <= 50');
cbo.Items.Add('> 50 & <= 75');
cbo.Items.Add('> 75');
cbo.OnChange := DoComboChange;
end;
procedure TForm1.DoComboChange(Sender: TObject);
var
cbo: TComboBox;
f: TTMSFNCDataGridDataFilterData;
begin
cbo := TComboBox(Sender);
Grid.RemoveFilter;
f := Grid.Filter.ColumnFilter[Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress')];
f.Condition := cbo.Text;
Grid.ApplyFilter;
end;

Chaining Filters
With the filter row as an option on top of the already built-in filtering features there are plenty of ways to browse through the data. If visual filtering is not applicable to your application, programmatic filtering can be an option and in this area we provide a way to chain filter operations together. Let's take the following example, where we find if the Name contains 'k', the Status equals 'Abroad' and the Progress is smaller than 50.
Grid.ClearFilter;
Grid.Filter.Add(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Name'), gftContains, 'k')
.&And(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Status'), gftEqual, 'Abroad')
.&And(Grid.ColumnIndexByHeader('Progress'), gftSmallerThan, '50');
Grid.ApplyFilter;

Conclusion
TMS FNC Data Grid offers powerful filter options including a filter row. This feature allows you to quickly narrow down the data you are interested in. TMS FNC Data Grid is part of the .
